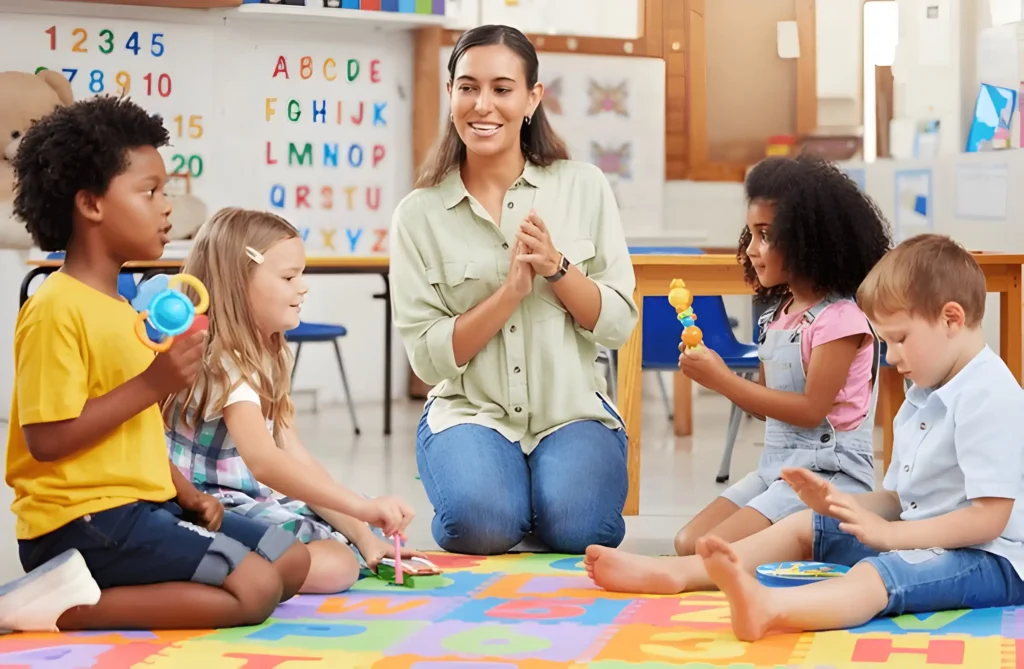

Preschool-aged children are like sponges—absorbing information from their surroundings with incredible speed and curiosity. This is a critical time for their development, as the brain rapidly forms connections that will influence future learning. Ensuring that the learning methods used during these formative years are both engaging and educational is key to laying a solid foundation for lifelong learning. While there are numerous educational philosophies and methods, some strategies stand out for their ability to stimulate creativity, problem-solving, social development, and cognitive growth.
The Importance of Early Childhood Education
The early years are often referred to as a “sensitive period” for development. Research shows that preschool-aged children learn best when exposed to an environment rich in opportunities for play, exploration, and social interaction. Cognitive functions, such as language, memory, and reasoning, begin to flourish when children are exposed to structured yet flexible learning activities. Education at this stage isn’t just about learning facts; it’s about nurturing emotional intelligence, resilience, and curiosity that will shape a child’s future.
Characteristics of Preschool-Aged Children
Understanding the unique developmental characteristics of preschool-aged children is essential to implementing the right learning methods. At this stage, children are developing rapidly in several key areas:
- Cognitive Development: Children begin to form logic, understand patterns, and solve simple problems.
- Social Skills: They learn to interact, share, and communicate with peers.
- Emotional Regulation: Emotional development takes off as they learn to express and manage their feelings.
- Motor Skills: Fine and gross motor skills improve, allowing for better coordination and control.
The best learning methods align with these developmental milestones, offering activities that meet preschoolers where they are in their growth journey.
Play-Based Learning
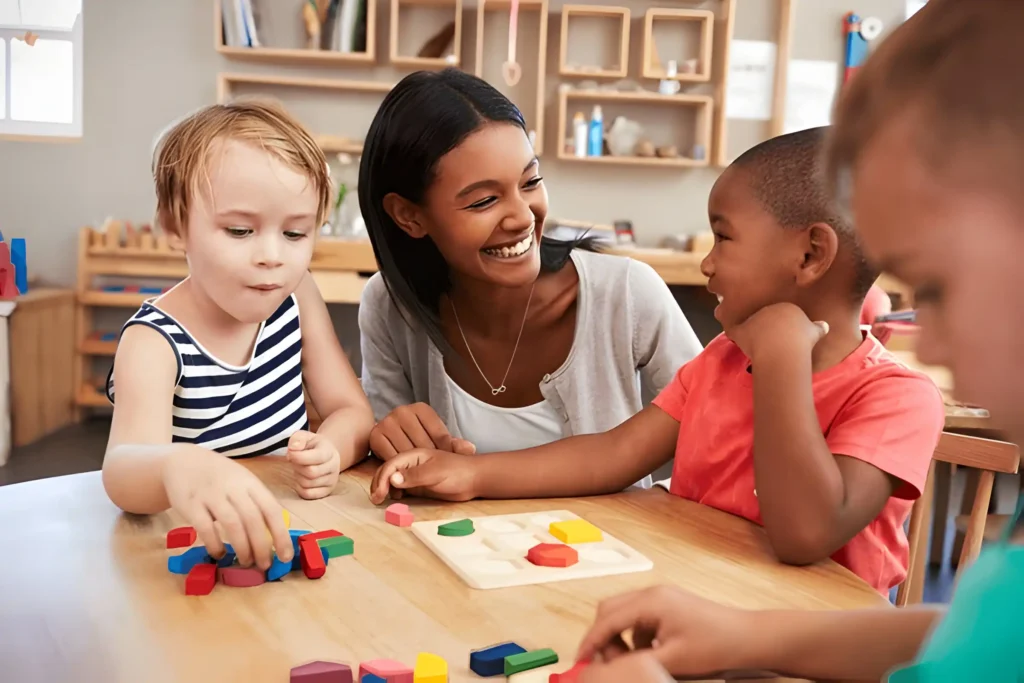

Play is the language of preschool-aged children. It’s how they explore, understand, and process the world around them. Play-based learning has been shown to foster imagination, creativity, and problem-solving abilities in young children. Through guided play, children practice new skills, make connections between concepts, and even develop social skills by interacting with peers.
Play-based learning often looks like games, role-playing, and hands-on activities where children can manipulate objects, experiment, and discover new things. Importantly, it taps into their natural curiosity, making learning enjoyable rather than a chore. In this setting, educators serve as facilitators, guiding children gently toward understanding rather than dictating rigid lessons.
Montessori Method
The Montessori method, pioneered by Dr. Maria Montessori, emphasizes self-directed learning. In Montessori classrooms, children are given a variety of hands-on learning materials and the freedom to choose activities that interest them. The idea is that children learn best when they’re interested and invested in what they’re doing. This method helps to foster independence, concentration, and a sense of responsibility in preschoolers.
Montessori’s focus on real-world tasks, like pouring water or sorting objects, also supports the development of fine motor skills and practical life skills. Children in these environments learn at their own pace, with teachers offering gentle guidance without overwhelming instruction. The classroom environment is meticulously prepared to be child-friendly and promote autonomy.
The Reggio Emilia Approach
The Reggio Emilia approach takes a collaborative, project-based approach to early childhood learning. Originating in Italy, this philosophy views children as capable, curious individuals who learn best through exploration and inquiry. In Reggio Emilia classrooms, children often engage in long-term projects based on their interests, such as creating art, building structures, or exploring nature.
This method encourages a strong sense of community, as it values collaboration between children, teachers, and even parents. It’s a flexible, adaptive approach that evolves based on the needs and interests of the children involved. As a result, children develop not only cognitive skills but also a sense of belonging and confidence in their ability to contribute to group efforts.
Waldorf Education
Waldorf education, developed by Rudolf Steiner, emphasizes the importance of imagination and creativity in early childhood. In a Waldorf classroom, children engage in activities like storytelling, art, music, and imaginative play. The goal is to foster a sense of wonder and joy in learning while nurturing the whole child—emotionally, socially, and intellectually.
In addition to academic skills, Waldorf education promotes rhythm and routine, which provide a comforting and predictable structure for young learners. The focus on creative expression helps children develop not only cognitive skills but also emotional intelligence and social awareness. This holistic approach is designed to cultivate well-rounded individuals with a deep connection to both their inner selves and the world around them.
Language Development Strategies
Language acquisition is one of the most critical skills preschool-aged children develop, and various methods can support this growth. Engaging children in conversation, reading aloud to them, and encouraging them to tell their own stories are simple yet effective ways to enhance language skills. Additionally, singing songs, playing word games, and introducing new vocabulary during playtime can help enrich their linguistic abilities. It’s crucial to create a language-rich environment where children are constantly exposed to new words and sentence structures.
Visual and Sensory Learning
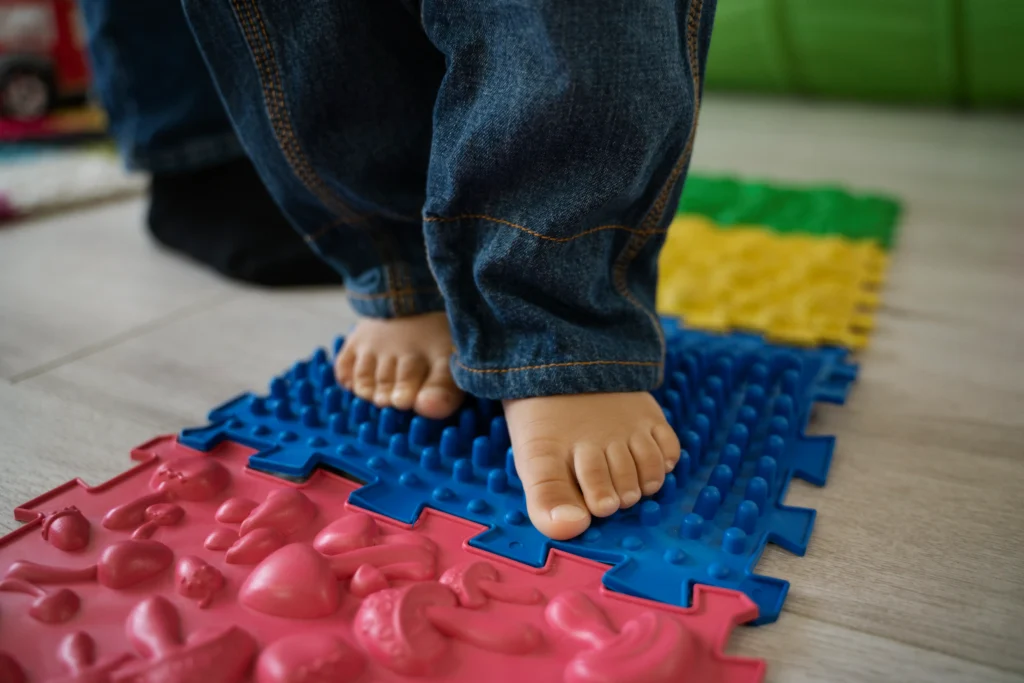

Preschoolers rely heavily on their senses to explore the world, making visual and sensory learning crucial for this age group. Activities that involve touch, smell, sight, sound, and even taste can stimulate brain development. For example, sensory bins filled with different textures or colors can spark curiosity and teach children about categorization, pattern recognition, and sensory processing.
Using visual aids like picture books, flashcards, and colorful educational materials can also enhance memory retention and make abstract concepts more concrete. Preschoolers often respond well to bright colors, simple shapes, and interactive visuals that invite them to touch, move, or manipulate objects.
Learning through Music and Movement
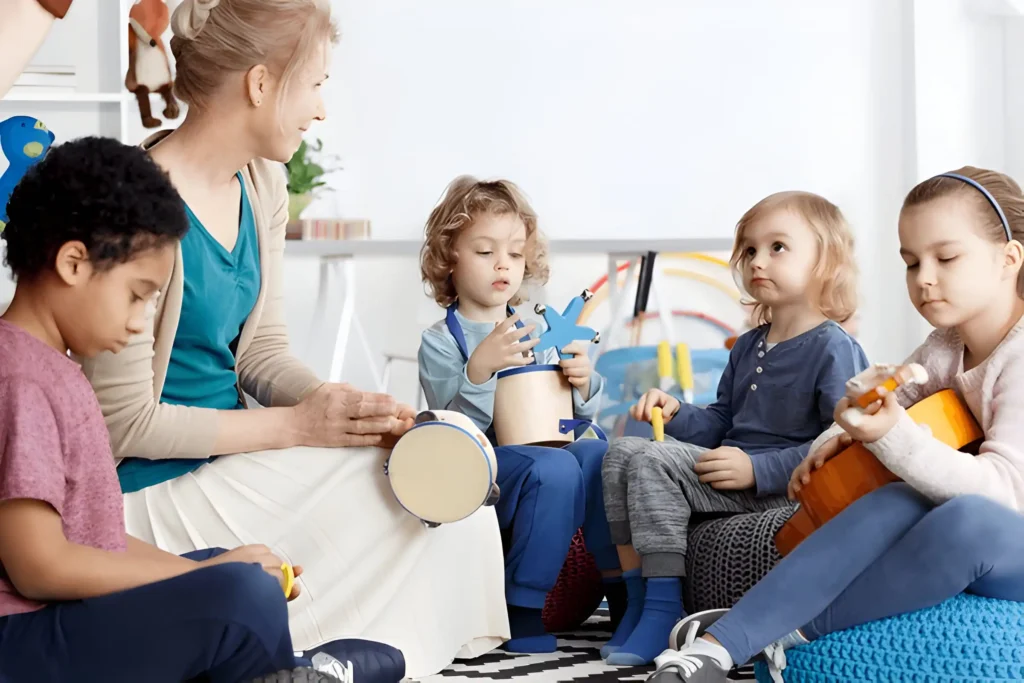

Music and movement are powerful tools for learning in preschoolers, as they combine cognitive development with physical activity. Singing songs, dancing, and engaging in rhythmic activities help children develop listening skills, coordination, and a sense of timing. Research has shown that music can also enhance memory, improve attention spans, and foster creativity.
Simple musical games like clapping rhythms, playing instruments, or dancing to the beat can teach children concepts like counting, patterns, and even early math skills. Additionally, incorporating movement into learning can help preschoolers burn off energy while also improving their motor skills and concentration.
The remaining sections will continue from this base, with each strategy further explored and detailed for a holistic view of the best learning methods for preschool-aged children.
FAQs
How important is play for preschool-aged children?
What is the Montessori method and how does it benefit young learners?
How can parents support language development in preschoolers?
What role does sensory play have in early childhood learning?
Is it safe for preschoolers to use technology for learning?
How can educators create a positive learning environment for preschoolers?
Conclusion
The preschool years are a critical time for laying the groundwork for future learning. By using a variety of methods—from play-based learning to structured educational approaches like Montessori or Reggio Emilia—parents and educators can help children develop essential cognitive, social, and emotional skills. Each child is unique, and the best learning methods are those that adapt to individual needs while fostering a love for learning.





Trackbacks/Pingbacks